A virtual private cloud (VPC) is a virtual network dedicated to your AWS account. It is logically isolated from other virtual networks in the AWS Cloud.
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network. You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs, or with a VPC in another AWS account. The VPCs can be in different Regions (also known as an inter-Region VPC peering connection).
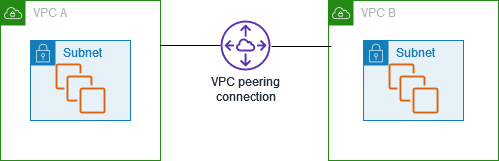
Figure 1
A VPC peering connection helps you to facilitate the transfer of data. For example, if you have more than one AWS account, you can peer the VPCs across those accounts to create a file sharing network. You can also use a VPC peering connection to allow other VPCs to access resources you have in one of your VPCs.
Multiple VPC peering connections
A VPC peering connection is a one to one relationship between two VPCs. You can create multiple VPC peering connections for each VPC that you own, but transitive peering relationships are not supported. You do not have any peering relationship with VPCs that your VPC is not directly peered with.
The following diagram is an example of one VPC peered to two different VPCs. There are two VPC peering connections: VPC A is peered with both VPC B and VPC C. VPC B and VPC C are not peered, and you cannot use VPC A as a transit point for peering between VPC B and VPC C. If you want to enable routing of traffic between VPC B and VPC C, you must create a unique VPC peering connection between them.
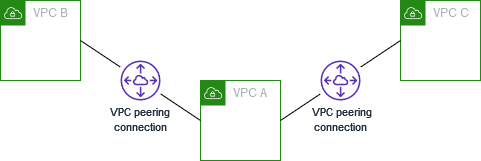
Figure 2
Click Here to Learn About VPC Peering Scenarios
